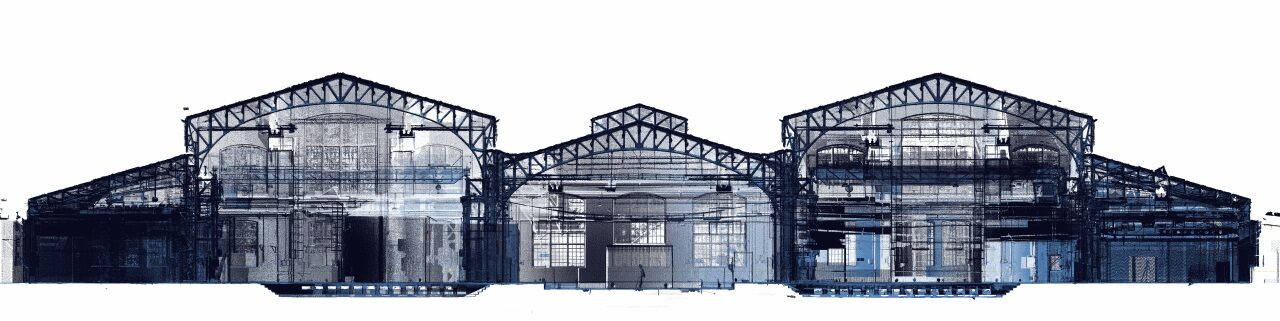
3D lézer szkennelés az építészetben, épületfelmérés
Amit kínálunk:
- Technológiai tanácsadás
- Meglévő épületek, épületrészek 3D lézer szkennelése, felmérése
- Homlokzatok, belső terek lézer szkenneres felmérése
- GNSS alapú bemérés és kitűzés
- Pontfelhő feldolgozás
- 3D modellezés
- 2D építészeti rajzok, ortofotók készítése
- Megvalósulási dokumentáció előállítása
- Minőség-ellenőrzés
- Monitoring
- Környezet felmérése
- Látványtervezés
- BIM (Building Information Management)
- Szintvonalas térkép készítés
- Épületrekonstrukció
- 3D nyomtatás
Építész katalógus
http://issuu.com/mensor3d/docs/mensor3d_epiteszet_oldal
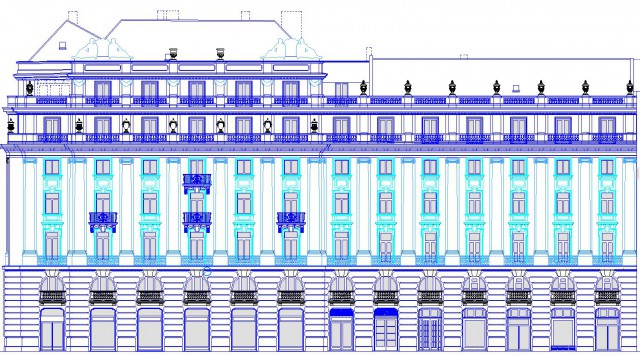
Kossuth tér 9-10
A 3D szkennelés előnyei
- Hatékony kivitelezés tervezés és megvalósulás ellenőrzés
- A színtérképes megjelenítésnek köszönhetően a hibák gyorsabban korrigálhatók
- Előzetes kivitelezhetőségi elemzés és ütközésvizsgálat
- Mennyiségszámítás és a költségbecslés
- Lehetőség a megvalósítási helyszíntől eltérő precíz előgyártásra
- A kivitelezési tevékenységek ellenőrzése, tanácsadás és nyomon követés
- A megvalósítási terület gyorsan felmérhető – a hagyományos módszereknél rövidebb idő alatt pontosabb, részletgazdagabb felmérés
- Az adatállomány megmarad, így az a későbbiekben bármikor, bármilyen eredménytermék előállítására alkalmas, a később felmerülő igényekre is felhasználható
- A pontfelhő alternatívák és hipotézisek vizsgálatára is használható, újabb helyszíni felmérések elvégzése nélkül
- Interdiszciplináris kutatást lehetővé tevő adatállomány áll elő
- Felszínkapcsolatok felmérhetők
A 3D szkennelés, 3D digitalizálás előnyei
A 3D technológiák elterjedése
A háromdimenziós technológiák, mint a térbeli tervezés, képalkotás, megjelenítés vagy nyomtatás forradalmi fejlődésen mennek keresztül napjainkban.
Az egyre fejlettebb eszközök (pl. szkennerek, nyomtatók, monitorok), illetve szoftverek (digitalizáló, CAD/CAM/CAE programok) újabb és újabb felhasználási területeket nyernek meg az ipar, az építészet, az élettudományok, a kultúra, vagy éppen a szórakoztatás terén.
3D lézer szkennelés, 3D digitalizálás
A három dimenziós szkennelés alapvetően a fizikai kiterjedéssel rendelkező testek (az építészetben pl. épületek, építmények) digitális állománnyá való konvertálását jelenti. A szkennerek a geometriai alakzat teljes felületét leképezik pont- vagy poligonfelhő formájában, mindezt úgy, hogy maga az eszköz nem ér hozzá az objektumhoz.
Az így előállt adathalmazt speciális, az eszköz mellé tartozó szoftverekkel lehet feldolgozni és előkészíteni a további feladatok végrehajtásához (pl. monitoring, minőség-ellenőrzés, hiteles rekonstrukció).
A legkorszerűbb földi lézer szkennerek akár 1 millió pontot is képesek letapogatni egyetlen másodperc alatt. A felvett pontok sűrűsége, egymástól mért távolsága a feladattól függően változtatható. A földi lézerszkenneres felmérés eredményének az egységes országos vetülethez (EOV) való kapcsolását GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) vevő alkalmazásával oldjuk meg. Az általunk használt földi szkennerek lézere Class I-es besorolásúak, tehát nem jelentenek veszélyt az emberi egészségre.
A 3D szkennlés során készített pontfelhőállományok és nagy felbontású digitális fényképek az épületek teljesebb és pontosabb dokumentálását teszik lehetővé.
3D technológia megoldások
Minőség-ellenőrzés (Quality Control)
A minőség ellenőrzéshez használt hagyományos mérési technikák időigényesek és drágák lehetnek. Ebben segíthet a 3D szkenneléssel előállított modell és a kiindulási CAD adatok összehasonlítása, ellenőrzése. A minőség ellenőrzés eredményeként elálló mérési jegyzőkönyv része egy színtérképes megjelenítés, amely vizuálisan jól elkülöníthetően mutatja a tervtől való eltéréseket. Így nem csak azt lehet meghatározni, hogy a már megépített épületrészek megfelelő kivitelezésben készültek-e el, hanem azt is, hogy hol kell azt esetlegesen módosítani.
Tervezési hibák csökkentése ütközésvizsgálattal
Minden kivitelező számára kritikus munkafolyamat a szakmák és a rendszer összehangolása. A hagyományos, 2D-s koordinációs megoldások lassúak, költségesek, nagy bennük a hibalehetőség és használatuk nagyban függ a rajzok naprakész voltától. A BIM alapú ütközés vizsgálati eszközök lehetővé teszik az automatikus geometria alapú ütközésvizsgálat kombinálását a szemantikai és szabály alapú ütközéselemzéssel a minősített és strukturált ütközések azonosítására.
BIM (Building Information Modelling)
A BIM egy létesítmény fizikai és funkcionális jellemzőinek digitális reprezentációja, a legújabb generáció az OOCAD rendszerek sorában, amelyben az épület tervét az összes intelligens épületobjektum összessége adja. A Building Information Model egy egységes, logikus, következetes forrása minden, az épülethez kapcsolódó adatnak. A BIM megbízható alapul szolgál a vezetői döntések meghozatalához az épület, létesítmény teljes életciklusa alatt, mely a szabvány meghatározás szerint a legelső koncepció kialakításától az elbontásig tart. A lézeres 3D szkennelést hatékonyan fel lehet használni helyreállítási munkálatokhoz és szerkezeti elemek megvalósulásának dokumentálásához is.
Szolgáltatásaink előnyei
- Nem szükséges drága eszközöket vásárolnia a szkenneléshez, feldolgozáshoz
- Az adott feladathoz leginkább megfelelő, piacvezető cégek eszközeit használjuk
- Tapasztalt, felkészült munkatársakkal dolgozunk
[:en]
3D scanning in architecture
We offer:
- Technological consulting
- 3D scanning and assessment of finished buildings and part of buildings
- 3D survey of facades and interiors
- GNSS based survey and stakeout
- Point cloud processing
- 3D modelling
- Preparation of 2D floor plans, cross sections and orthophotos
- Preparation of as-built documentation
- Quality controll
- Monitoring
- Environmental assessment
- Visualization
- BIM (Building Information Management)
- Preparation of contour maps
- Building reconstruction
- 3D printing
Advantages of 3D scanning
- Effective construction scheduling and implementation monitoring
- Thanks to the colour map visualization, faults can be corrected more quickly
- Preliminary feasibility analysis and clash detection
- Quantity calculation and cost estimation
- The scanned data set showing the original state of a building and the planned model can be displayed together
- Control of the building activity, consulting and tracking
- The building site can be assessed rapidly; more detailed results in less time, compared to traditional methods
- The data file is lasting and will be available any time to facilitate any kind of end result, or to be used in the course of fulfilling future demands
- The point cloud can also be used to inspect alternatives and hypotheses without the need to realize further local assessments
- The data file created also facilitates interdisciplinary research
- The surface connections can also be traced
Spread of 3D technologies
3D technologies such as in-space planning, spatial visualization and displays, or spatial printing are currently going through a revolutionary development.
More and more advanced instruments (such as scanners, printers, monitors), and software (digitalizing and CAD/CAM/CAE software) are gaining more and more application areas within the fields of industry, life sciences, culture and entertainment,
3D scanning, 3D digitalizing
3D scanning is essentially converting physical objects (like products, instruments in mechanical engineering) into digital data files. Scanners map the whole surface of the geometrical shape into a point cloud or polygon cloud without touching the object itself.
Special software available with the equipment can be used to process the resulting data file and to prepare it for further tasks (such as reverse engineering or quality control).
The most advanced terrestrial laser scanner can record up to one million points a second. The density and distance between the mapped points can be altered in the function of the job in question. We use a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver to connect the results of the terrestrial laser scanning to the unified national orthography (abbreviated as EOV). The lasers in the terrestrial scanners we use are classified as Class I, meaning that they are not harmful to human health.
The point cloud data sets and high resolution digital photographs obtained in the process of 3D scanning facilitate fuller and more accurate documentation of buildings.
3D technology solutions
Quality Control
Traditional measuring technologies used in quality control can be time consuming and expensive. This is where comparison and verification of the 3D scanned model and the original CAD data can help. The comparison report, prepared as a result of the quality control, includes a colour-mapped visualization, which shows all points of deviation from the plan in an easily identifiable manner. Apart from the ability to decide whether the parts of the structure that have already been built have been done so appropriately, it is also possible to define where modifications should be made.
Reduction of planning faults with clash detection
The coordination of trade and the system is a critical work procedure for every building constructor. Traditional 2D coordination solutions are time consuming, costly, prone to faults and their use is highly dependent on how up-to-date the plans are. The BIM based clash detection instruments facilitate the combination of automatic, geometry based collision inspections with semantic and rule based collision analysis to identify qualified and structured collisions.
Building Information Modelling
BIM is the digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a facility. It is the newest generation of OOCAD systems, in which building plans are identified as the entirety of all intelligent building objects. The Building Information Model is a unified, logical and coherent source of all data related to the building. The BIM is a reliable basis for managerial decisions throughout the whole life cycle of the facility, which extends, based on a standard definition, from the elaboration of the first concept to the demolition of the building. 3D laser scanning can be used effectively both in recovery works and for the documentation of building structural elements.
Architect Catalog
http://issuu.com/mensor3d/docs/mensor3d_architecture
Our services advantages
- No need to purchase expensive equipment for scanning and processing tasks
- We use equipment from market leading companies, which are best suited to the specific task
- We work with experienced, trained personell
[:de]
3D-Scannen in der Architektur
Wir bieten:
-
- Technologische Beratung
- 3D-Scannen und Bewertung der fertigen Bauten und Teile von Gebäuden
- 3D-Vermessung von Fassaden und Innenräume
- GNSS basierte Umfrage und Absteckung
- Punktwolkenverarbeitung
- 3D-Modellierung
- Herstellung von 2D-Grundrisse, Querschnitte und Orthophotos
- Herstellung von As-Built-Dokumentation
- Qualitätskontrolle
- Überwachung
- Umweltprüfung
- Visualisierung
- Gebäudedatenmodellierung
- Herstellung von Konturkarten
- Gebäudesanierung
- 3D Druck
Wir verwenden Z+F und Leica (basierend auf Z+F) Laserscanner. Die 3D Laserscanner ermöglichen eine schnelle, lückenlose und exakte 3D-Dokumentation des Ist-Zustandes von Gebäuden oder komplexen Bauwerken und deren gesamter Umgebung. Man erhält ein exaktes räumliches Modell, was die Qualität bei der Realisierung von Projekten enorm erhöht.
Aus den 3D-Messdaten lassen sich darüber hinaus 2D-Pläne wie Grundrisse, Frontansichten oder Höhenschnitte für spätere Neu- und Umbaumaßnahmen erstellen. Die gescannten 3D-Daten bilden daher eine ideale Planungsgrundlage für bauliche Maßnahmen. Auch ein verformungsgerechtes Aufmaß, welches von den Bauämtern für die Antragsplanung oft gefordert wird, lässt sich mit den Laserscannern zügig erstellen.
Durch die Bestandsaufnahme mit einem Laserscanner sparen Sie nicht nur Zeit und Kosten bei Aufmaßarbeiten, sondern haben auch die Möglichkeit, verschiedene Varianten zur Nutzung von bestimmten Räumlichkeiten durchzuspielen, ohne diese Räume in der Realität begehen zu müssen. Sie können alles bequem von Ihrem Arbeitsplatz aus erledigen. Darüber hinaus haben Sie auch noch Jahre später die Möglichkeit, auf Ist-Daten wie Massen oder Maße zurückzugreifen.
Bauschäden
Bauschäden bedeuten für den Eigentümer und Nutzer von Gebäuden Unannehmlichkeiten und oft einen erheblichen wirtschaftlichen Schaden. Sie können den Wert und den Ertrag einer Immobilie aktuell und in Zukunft erheblich beeinträchtigen. Werden folglich bei der Bestandsaufnahme durch die Laserscanner bauliche Abweichungen vom Auftrag oder Mängel erfasst, kann rechtzeitig gegengesteuert werden, was ebenfalls zu erheblichen Kosteneinsparungen führt.
Die Vorteile von 3D-Scannen
Erstellen von 3D-Modellen
Aus den Daten der phasenbasierten Laserscanner lassen sich mithilfe der Software LFM semiautomatisiert 3D-Modelle des Ist-Zustandes einer Fabrik oder einer Anlage generieren (z. B. Rohre, Stahlträger etc.). Darüber hinaus ist eine komplette Generierung von CAD-Modellen aus den 3D-Scandaten möglich.
Kollisionsprüfung
Die 3D-Modelle ermöglichen es, Produktionsabläufe zu simulieren und Kollisionsprüfungen durchzuführen. Beispiel: In eine bestehende Anlage soll ein weiterer, baugleicher Produktionsroboter eingefügt werden.
Gebäudedatenmodellierung
Der Begriff Building Information Modeling (kurz: BIM; deutsch: Gebäudedatenmodellierung) beschreibt eine Methode der optimierten Planung, Ausführung und Bewirtschaftung von Gebäuden mit Hilfe von Software. Dabei werden alle relevanten Gebäudedaten digital erfasst, kombiniert und vernetzt. Das Gebäude ist als virtuelles Gebäudemodell auch geometrisch visualisiert (Computermodell). Building Information Modeling findet Anwendung sowohl im Bauwesen zur Bauplanung und Bauausführung (Architektur, Ingenieurwesen, Haustechnik) als auch im Facilitymanagement.
Facility Management
Alle feststehenden Einrichtungsgegenstände wie z. B. Leitungen und Rohre werden erfasst und in einer 3D-Datenbank abgelegt, die als Grundlage für spätere Umbaumaßnahmen dient. Eine Aktualisierung und Erweiterung dieser Datenbank ist jederzeit möglich.
Überwachung, Rekonstruktion
Auch bei denkmalgeschützten Bauwerken stellen sich regelmäßige Bauaufgaben. Oft aber existieren dabei keine ausreichenden Pläne, auf deren Grundlage geplant, modernisiert oder saniert werden kann. Aufgrund der sehr hohen Abtastrate von über 1 Mio. Messwerte pro Sekunde, Entfernungsauflösung im Submillimeterbereich und einer Messgenauigkeit im mm-Bereich ist selbst eine Erfassung von feinsten Strukturen und Details mit den 3D Laserscannern noch möglich. Die 3D-Dokumentation bildet daher die ideale Voraussetzung für Rekonstruktionen von beispielsweise gestalterischen Gegebenheiten oder sensiblen Stuckarbeiten. Die erfassten Bestände, Schäden, Strukturen und Details werden in Datenbanken festgehalten und erlauben eine originalgetreue Rekonstruktion des gesamten Objekts oder von Teilen des Objekts zu jedem späteren Zeitpunkt.